What is a Pressure Reducing Valve and How Does It Ensure System Efficiency
A pressure reducing valve (PRV) is an essential component in various fluid systems, designed to regulate and maintain the pressure within specific parameters, ensuring optimal performance and safety. By lowering and stabilizing high inlet pressure to a desired outlet pressure, a pressure reducing valve not only protects downstream equipment but also enhances overall system efficiency. Understanding how a PRV operates is crucial for engineers, technicians, and facility managers in various industries, as it directly impacts energy consumption, operational costs, and equipment longevity. This guide will delve into the mechanisms behind pressure reducing valves, their importance in maintaining system integrity, and best practices for their selection and installation, ultimately leading to a more efficient and reliable fluid management system.
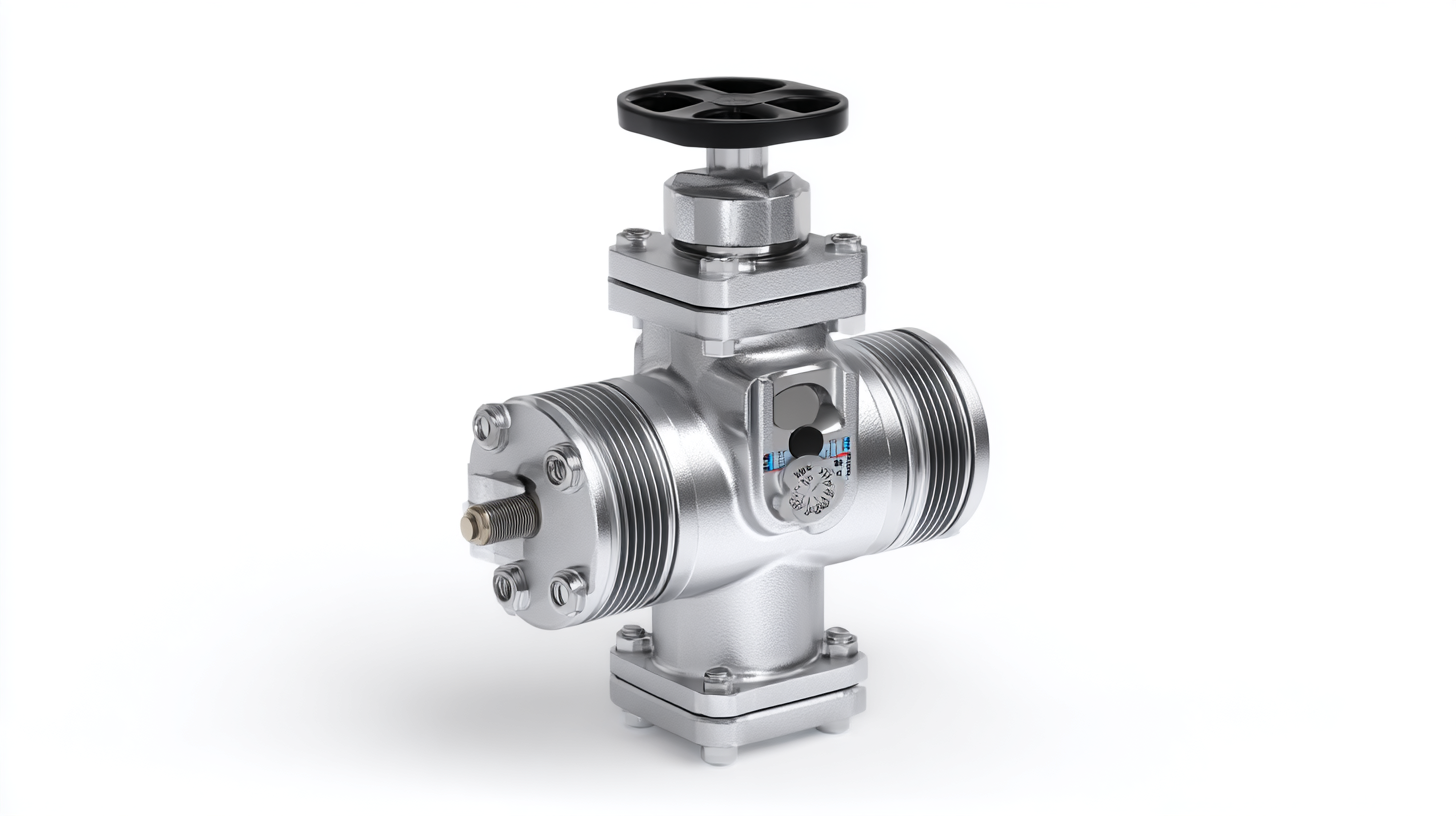

Understanding the Basics of Pressure Reducing Valves and Their Functionality
A pressure reducing valve (PRV) is a critical component in various fluid systems, designed to lower and regulate the pressure of a fluid from a higher inlet pressure to a desired outlet pressure. This functionality is essential for protecting sensitive equipment from damage due to excessive pressure and for maintaining efficient system operation. PRVs are widely used in applications ranging from domestic water supply systems to industrial processes, ensuring a consistent and safe pressure level for downstream devices.
Understanding how a PRV operates involves recognizing its primary components, typically including a valve body, a diaphragm or piston, and a spring mechanism. When fluid enters the valve at high pressure, it acts against the diaphragm. As the pressure rises above the set limit, the diaphragm moves to close the valve partially, thereby reducing the flow and maintaining a steady outlet pressure. This not only enhances the longevity of the system components but also contributes to energy efficiency by minimizing the need for hydraulic power, making pressure reducing valves integral to both safety and performance in fluid dynamics.
Key Benefits of Using Pressure Reducing Valves in Various Systems
Pressure reducing valves (PRVs) play a crucial role in various systems by maintaining optimal pressure levels and ensuring efficiency. One of the key benefits of using PRVs is their ability to protect downstream equipment from potential damage caused by excessive pressure. By regulating the pressure, these valves help extend the lifespan of pipelines, pumps, and fixtures, ultimately reducing maintenance costs and preventing unexpected shutdowns.
Another significant advantage of incorporating PRVs in systems is their impact on energy efficiency. By controlling and stabilizing pressure, PRVs minimize energy consumption, particularly in hydraulic systems where excessive pressure can lead to increased operational costs. Additionally, improving system efficiency often results in reduced water wastage in plumbing systems, making PRVs an environmentally friendly solution as well. Overall, the use of pressure reducing valves not only enhances system reliability but also contributes to cost savings and sustainability.
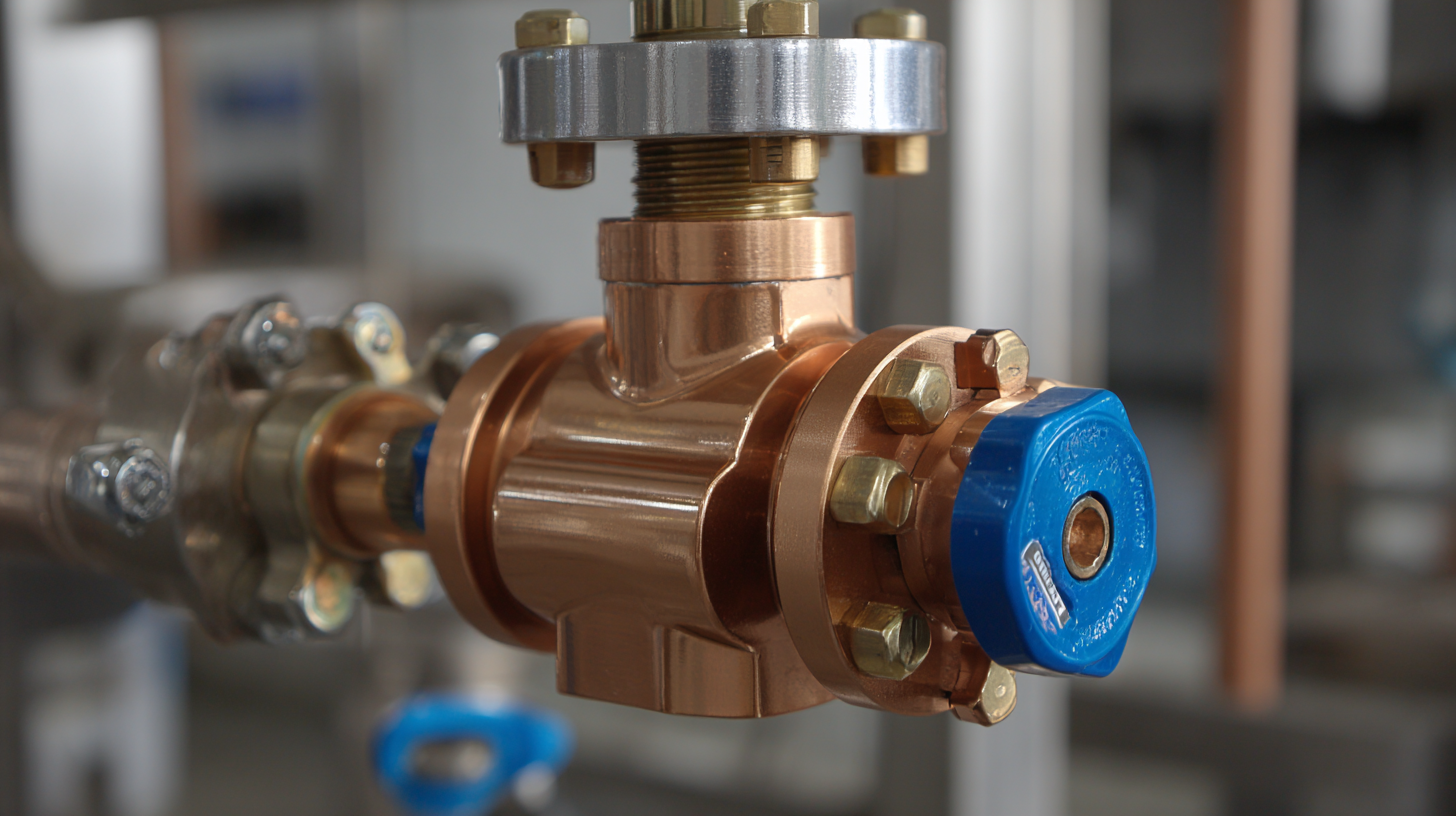
How Pressure Reducing Valves Enhance Overall System Efficiency
Pressure reducing valves (PRVs) play a crucial role in enhancing the overall efficiency of fluid systems across various industries. By maintaining a consistent downstream pressure, they prevent issues caused by excess pressure, such as leaks, equipment failure, and energy waste. According to a report from the Hydraulic Institute, implementing PRVs can lead to a 15-20% reduction in energy consumption for hydraulic systems, highlighting their significance in optimizing performance.
Moreover, PRVs contribute to system longevity by mitigating the risks associated with pressure fluctuations. High-pressure circumstances can lead to increased wear and tear on components, ultimately reducing their lifespan. A research study published by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) indicates that properly calibrated PRVs can extend the operational life of equipment by 30%, reinforcing the idea that efficient pressure regulation is essential for effective system management.
In industrial applications, the proper selection and installation of PRVs not only bolster efficiency but also enhance safety. The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) asserts that adequately managed systems are 40% less likely to encounter critical failure incidents. By integrating PRVs, organizations can achieve both operational efficiency and increased safety, fostering a more resilient infrastructure.
Factors Influencing the Performance of Pressure Reducing Valves
Pressure reducing valves (PRVs) are crucial components in managing fluid systems, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency. Various factors can significantly influence the operational efficiency of these valves. One primary factor is the inlet pressure; data from the International Association for the Properties of Water and Steam indicates that maintaining an optimal inlet pressure between 50 to 85 psi can enhance the valve's responsiveness and longevity. Deviations from this range can lead to premature wear or operational failures, impacting overall system reliability.
Another vital consideration is the valve sizing and selection. According to the Hydraulic Institute, improper sizing can lead to cavitation and noise issues, reducing operational efficiency by up to 20%. Engineers must carefully evaluate flow requirements and select PRVs that match system specifications to prevent these issues. Additionally, temperature variations of the medium can also affect valve performance; for instance, high temperatures can cause thermal expansion, leading to misalignment and increased wear. Studies have shown that ensuring compatibility with the operating temperature range can mitigate these risks and bolster overall system performance.
Factors Influencing the Performance of Pressure Reducing Valves
This bar chart illustrates various factors that influence the performance of pressure reducing valves. The metrics shown include inlet pressure, outlet pressure, flow rate, temperature, and valve size, which are critical to ensuring system efficiency.
Maintenance Practices to Ensure Longevity of Pressure Reducing Valves
Regular maintenance of pressure reducing valves (PRVs) is crucial to ensure their longevity and efficient operation. One of the key practices is to perform routine inspections, where one should check for signs of wear, corrosion, or leaks. Visual inspections can help identify issues early, thus preventing more significant problems down the line. Additionally, keeping the valve clean from debris or scale build-up is essential, as these contaminants can hinder the valve’s performance and lead to premature failure.
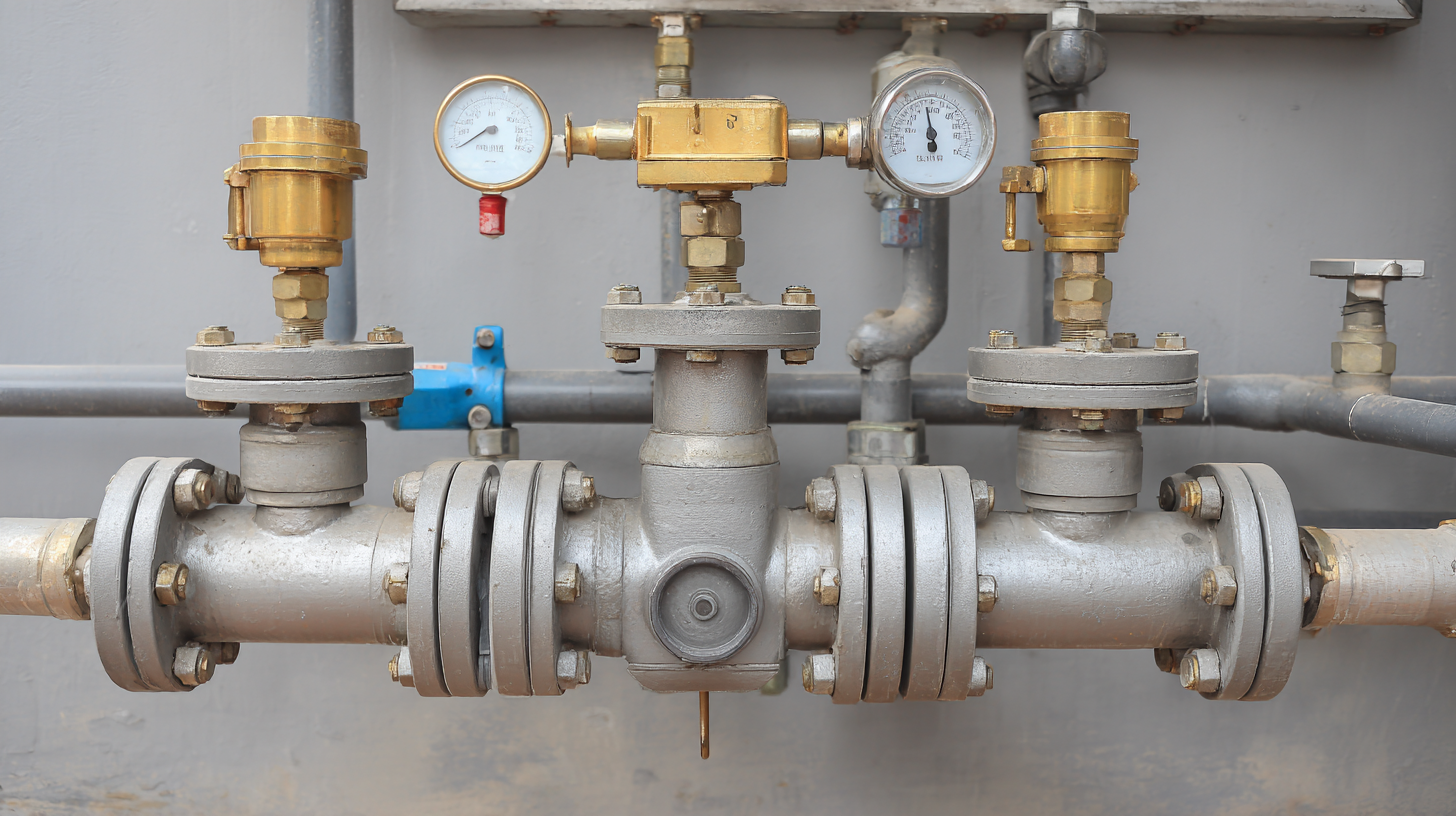

Another important aspect of maintenance is the calibration of the PRV. Over time, the set pressure may drift, so it is vital to recalibrate the valve periodically to ensure it maintains the desired output pressure. Furthermore, testing the functionality of the valve’s diaphragm and actuator can prevent unexpected failures. Proper lubrication of moving parts also plays a role in maintaining optimal performance. By adhering to these maintenance practices, one can significantly extend the lifespan of pressure reducing valves, ensuring their reliability and efficiency within the system.
Related Posts
-
How to Identify Top Quality Manufacturers for the Best Pressure Regulator
-

Common Issues Regarding Back Pressure Regulator Selection and Performance
-

Understanding Pressure Regulators for Optimal Performance in Industrial Applications
-

How to Optimize Your Systems with Pressure Control Valves for Maximum Efficiency
-
Unveiling China's Leading Electronic Pressure Regulators for Global Procurement Success
-
Understanding the Functionality of the Best Back Pressure Valve
