Understanding the Role of Back Pressure Valves in Modern Fluid Systems
In contemporary fluid systems, the back pressure valve plays a pivotal role in optimizing operational efficiency and ensuring system stability. According to recent industry reports, the global back pressure valve market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.3% from 2021 to 2026, driven by the increasing demand for automation and the need for reliable fluid control in various sectors such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and pharmaceuticals. Back pressure valves not only regulate the pressure within piping systems but also enhance the overall performance by preventing unwanted flow fluctuations. The implementation of these valves is crucial in maintaining desired pressure levels and safeguarding equipment, thereby reducing maintenance costs and extending service life.
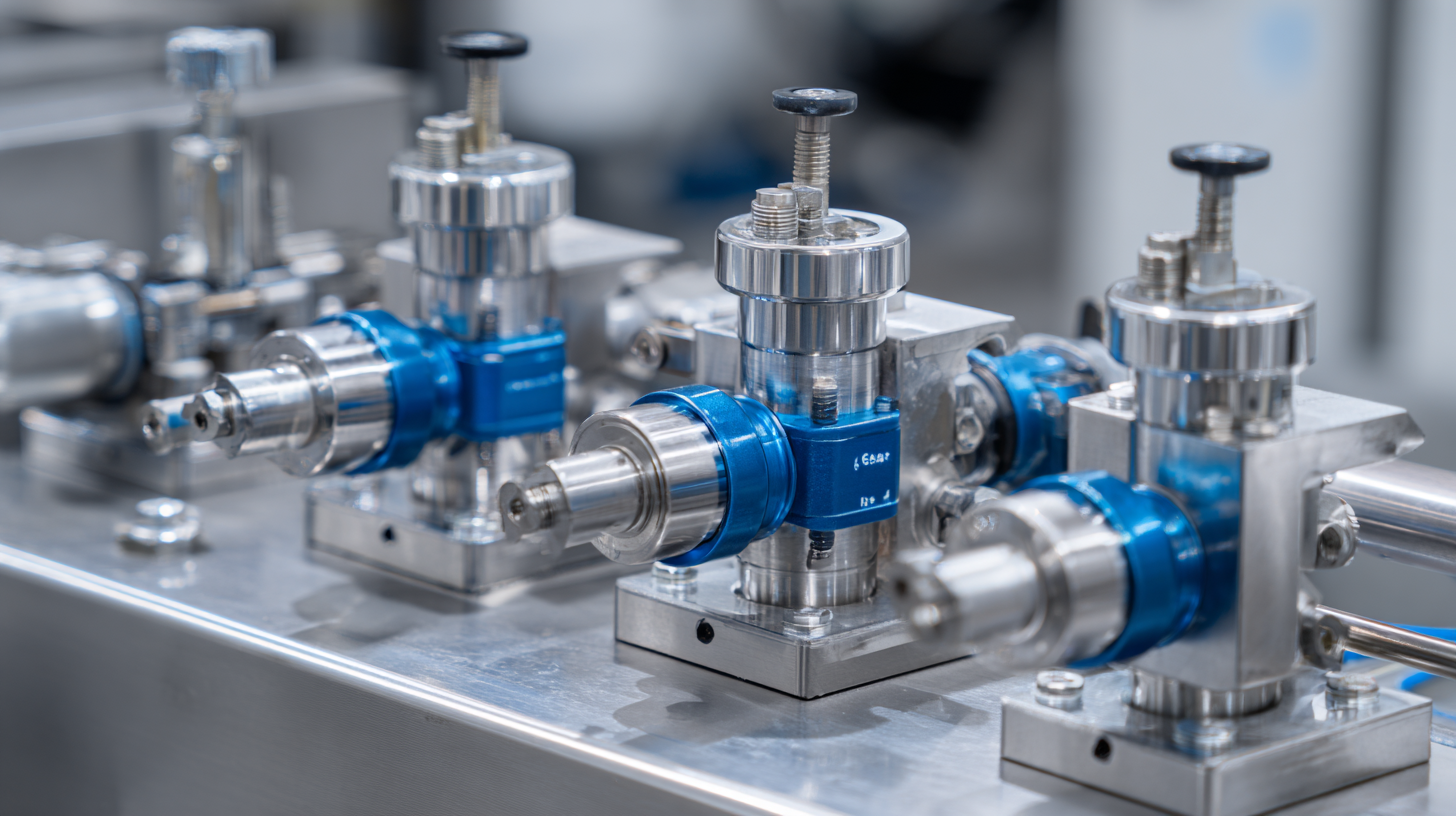

As fluid systems evolve, the significance of back pressure valves continues to rise, making them indispensable for modern engineering applications.
Definition and Function of Back Pressure Valves in Fluid Systems
Back pressure valves play a crucial role in modern fluid systems by maintaining a specific pressure level and ensuring the optimal performance of the system. These valves are typically installed in pipelines and process equipment to regulate the pressure upstream. Essentially, they prevent excessive pressure from building up, which can lead to equipment failure or unsafe operating conditions. According to a report by the Flow Control industry, back pressure valves contribute significantly to overall system efficiency, with estimates suggesting they can improve energy efficiency by up to 30% in certain applications.
The primary function of back pressure valves is to create a controlled resistance to fluid flow, thereby stabilizing downstream pressure. They are commonly employed in various industries, including oil and gas, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals. A technical paper from the Fluid Power Journal highlights that proper selection and sizing of back pressure valves are critical for maximizing the reliability and lifespan of fluid systems. It points out that failing to implement adequate back pressure management can result in operational costs escalating by an average of 15%, emphasizing the importance of these valves in maintaining both efficiency and safety in fluid handling processes.
Types of Back Pressure Valves and Their Applications
Back pressure valves play a critical role in modern fluid systems, serving to maintain the desired pressure levels and ensure system efficiency. There are several types of back pressure valves, each designed for specific applications. One common type is the spring-loaded back pressure valve, which relies on a spring mechanism to open and close based on pressure changes. According to a 2022 report by the Fluid Control Institute, this type is widely used in oil and gas refining, where maintaining optimal pressure is crucial for safety and operational efficiency.
Another prevalent type is the pilot-operated back pressure valve. This valve type uses a smaller pilot valve to control a larger main valve, enabling precise pressure regulation in complex systems. Industries such as pharmaceuticals and chemicals often utilize pilot-operated valves due to their ability to handle fluctuating pressures and maintain system stability, as highlighted in a recent market analysis that estimated a 6% CAGR for pilot-operated valves in these sectors over the next five years. Understanding the specific applications and characteristics of these valve types is essential for engineers and operators aiming to optimize fluid systems in various industrial contexts.
Understanding the Role of Back Pressure Valves in Modern Fluid Systems
| Type of Back Pressure Valve | Operating Principle | Applications | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spring Loaded Back Pressure Valve | Uses a spring to maintain pressure in the system. | Oil and gas applications, chemical processing. | Simple design, reliable performance. |
| Pilot-Operated Back Pressure Valve | Uses a pilot valve to control the main valve position. | Steam generation and power plants. | Better flow control, responsive to changes. |
| Equalizing Back Pressure Valve | Balances pressure between two points using a diaphragm. | Water distribution systems, irrigation. | Reduces water hammer effects. |
| Electronic Back Pressure Valve | Utilizes electronic controls for precise pressure regulation. | Pharmaceuticals, microelectronics. | High accuracy, programmable settings. |
Importance of Back Pressure Management in Industrial Processes
Back pressure management plays a critical role in the efficiency of industrial processes, significantly impacting the performance and longevity of fluid systems. In various sectors, including oil and gas, chemical manufacturing, and pharmaceuticals, maintaining optimal back pressure is essential to prevent equipment damage, ensure accurate flow rates, and enhance system reliability. A back pressure valve serves as a crucial component in regulating pressure within the system, allowing operators to control the fluid dynamics effectively.
Improper back pressure can lead to a host of problems, from reduced process efficiency to catastrophic failures. By correctly managing back pressure, industries can optimize their operations, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. This management is particularly vital in systems where variations in fluid density, temperature, and viscosity can cause fluctuations in pressure. Ultimately, effective back pressure control not only ensures the smooth functioning of industrial processes but also contributes to safety and compliance with regulatory standards, fostering a more sustainable manufacturing environment.
Understanding the Role of Back Pressure Valves in Modern Fluid Systems
This bar chart illustrates the perceived importance of back pressure management in various industrial sectors. The data indicates that the pharmaceutical industry places the highest significance on back pressure management, highlighting its crucial role in ensuring process stability and product quality.
Factors Influencing Back Pressure Valve Performance
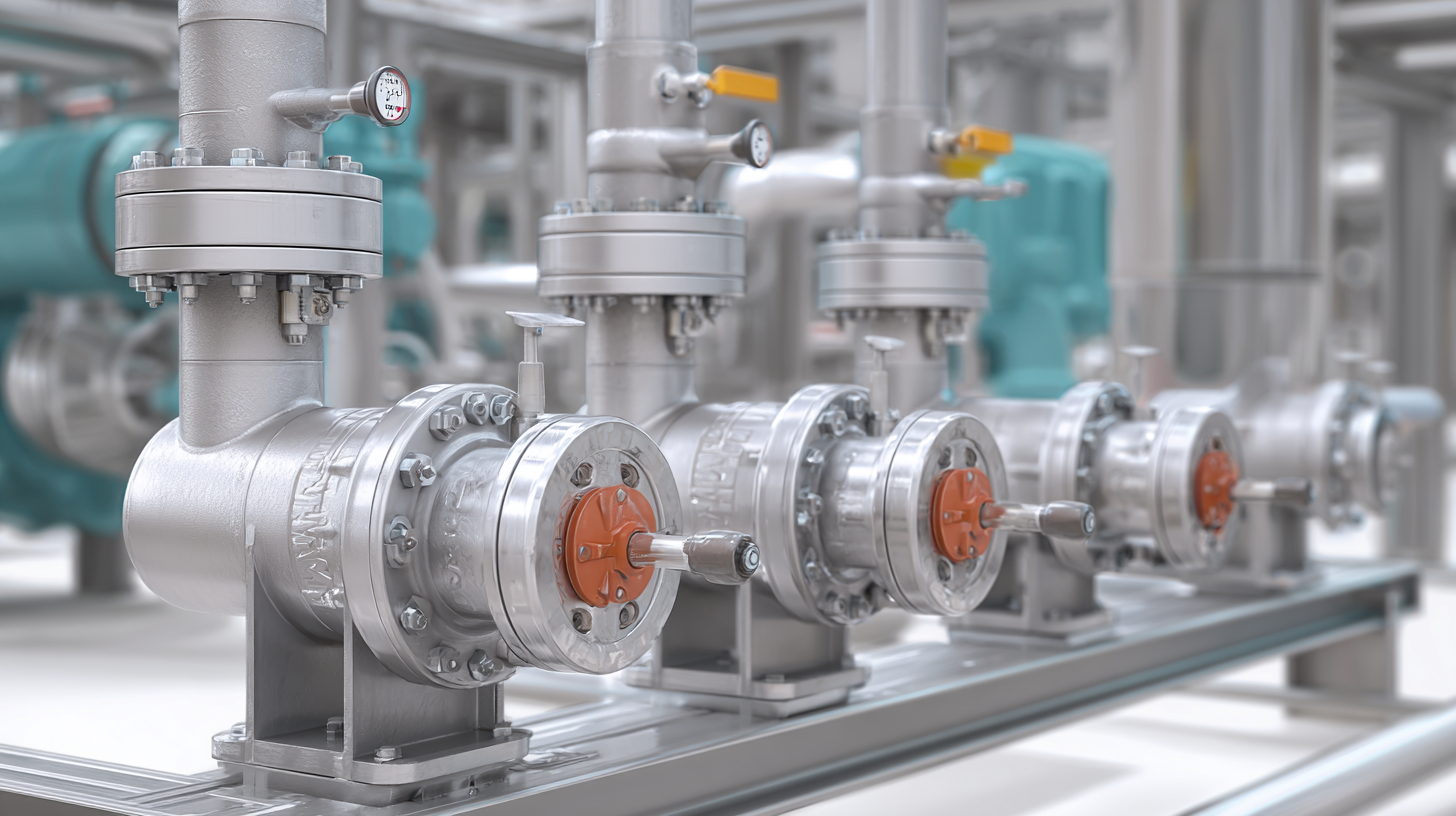 Back pressure valves are critical components in modern fluid systems, and their performance is influenced by various factors that must be carefully considered. One major factor is the fluid characteristics, including viscosity, temperature, and density. Fluids with higher viscosity may require a stronger pressure differential to operate effectively, impacting the valve's responsiveness. Additionally, temperature variations can alter the fluid's properties, leading to inconsistencies in valve performance. Understanding these characteristics helps engineers select the right back pressure valve for specific applications.
Back pressure valves are critical components in modern fluid systems, and their performance is influenced by various factors that must be carefully considered. One major factor is the fluid characteristics, including viscosity, temperature, and density. Fluids with higher viscosity may require a stronger pressure differential to operate effectively, impacting the valve's responsiveness. Additionally, temperature variations can alter the fluid's properties, leading to inconsistencies in valve performance. Understanding these characteristics helps engineers select the right back pressure valve for specific applications.
Another crucial factor is the system design, including the layout of piping and the overall pressure conditions. The valve's location within the system can significantly influence its effectiveness; valves placed too close to pumps or in areas with turbulent flow may not perform optimally. Moreover, the maintenance of the system plays a role in valve performance. Regular inspections and timely replacements ensure that the valves function correctly and do not suffer from issues like clogging or wear that could impede their operation. By considering these elements, engineers can enhance the reliability and efficiency of fluid systems, ensuring that back pressure valves operate at their intended capacity.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Back Pressure Valves
Back pressure valves are crucial components in modern fluid systems, ensuring optimal performance and safety. Maintenance of these valves is vital, as neglect can lead to significant operational issues. Regular inspections should include checking for any signs of wear, corrosion, or obstructions. According to the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), timely maintenance can reduce the likelihood of system failures by as much as 30%. This proactive approach helps maintain not only the functionality of the valves but also the overall efficiency of the fluid system.
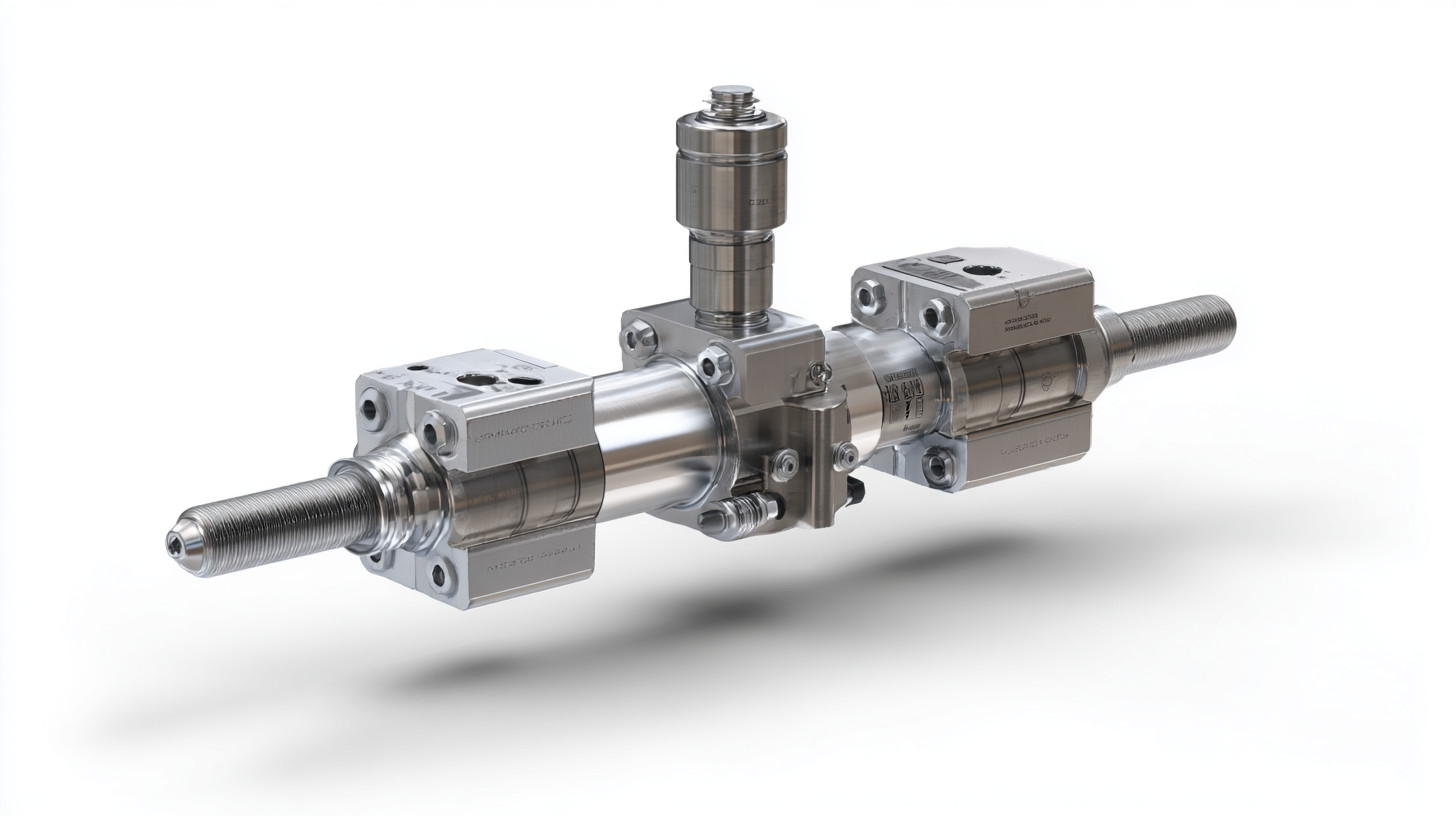
When troubleshooting back pressure valves, it is essential to identify common issues such as pressure spikes or irregular flow rates. A report from the International Association of Plumbing and Mechanical Officials (IAPMO) indicates that up to 25% of fluid system inefficiencies can directly be attributed to valve malfunctions, underscoring the importance of addressing these problems quickly. Utilizing diagnostic tools can streamline this process, allowing for precise identification of issues like valve seat leaks or actuator failures. By following a structured maintenance and troubleshooting routine, operators can enhance the longevity and reliability of back pressure valves, ultimately contributing to the smooth operation of fluid systems.
Related Posts
-
Understanding the Functionality of the Best Back Pressure Valve
-

Common Issues Regarding Back Pressure Regulator Selection and Performance
-
How to Identify Top Quality Manufacturers for the Best Pressure Regulator
-

Understanding Pressure Regulators for Optimal Performance in Industrial Applications
-

How to Optimize Your Systems with Pressure Control Valves for Maximum Efficiency
-

What is a Pressure Reducing Valve and How Does It Ensure System Efficiency
